In the challenging topography of hilly landscapes, breast walls stand as indispensable sentinels, exemplifying the fusion of engineering excellence and environmental adaptability. These structures, integral to hill road construction, play a paramount role in stabilizing slopes, mitigating erosion, and fortifying the very foundations of the landscape. A comprehensive understanding of the importance of breast walls unravels their significance in ensuring the safety, longevity, and resilience of hill roads.
Table of Contents
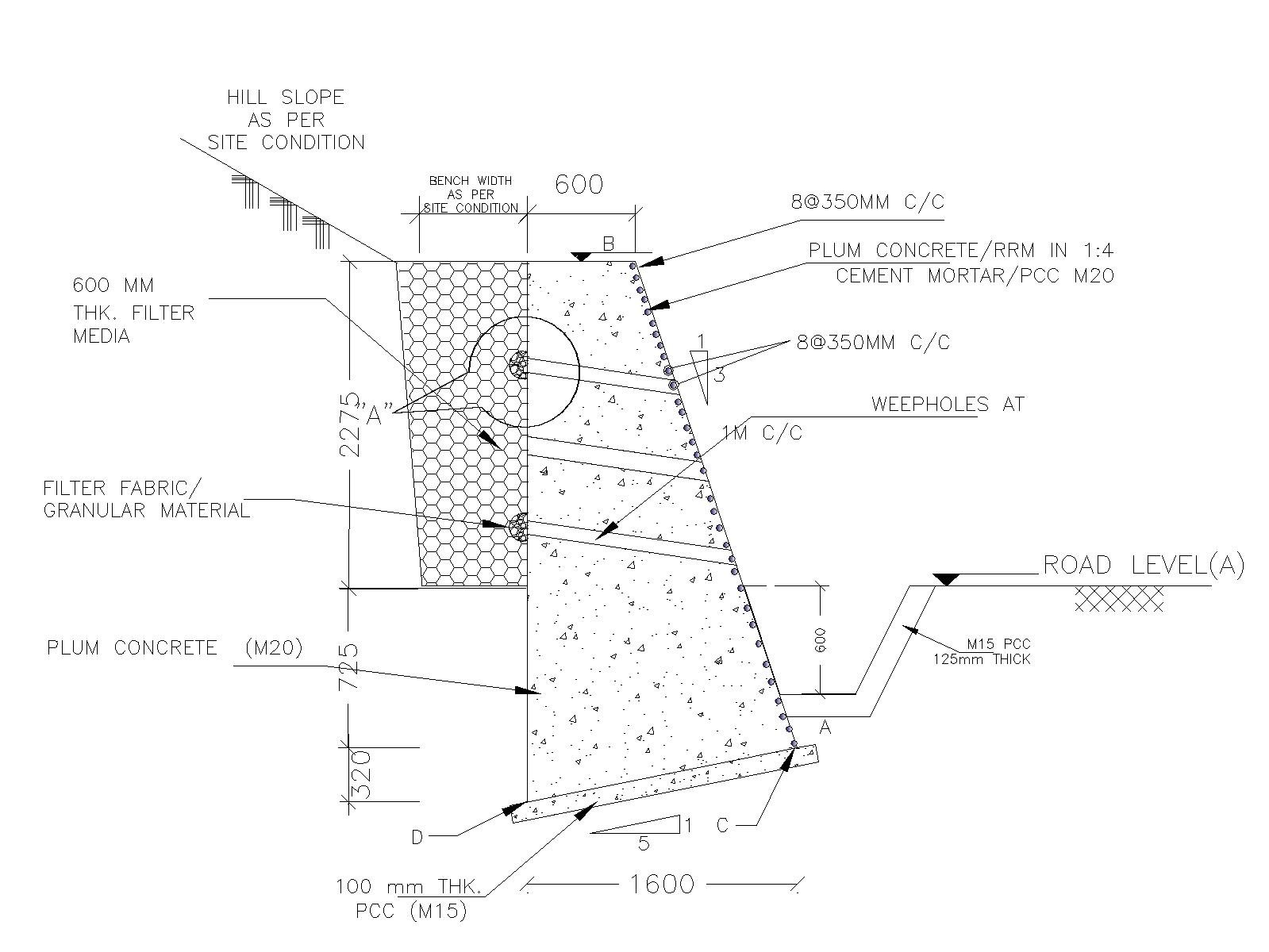
What is Breast Wall in Hill Roads?
The pivotal role of breast walls lies in their ability to counteract the natural forces that threaten the stability of steep slopes. Breast walls are crucial to mitigate the risks of landslides, erosion, and rockfalls that are brought on by the steep hillsides. These walls serve an important part in the sustainable development of hillside infrastructure by converting dangerous terrain into safe and comprehensible channels for both automotive and pedestrian traffic by strategically providing structural support.
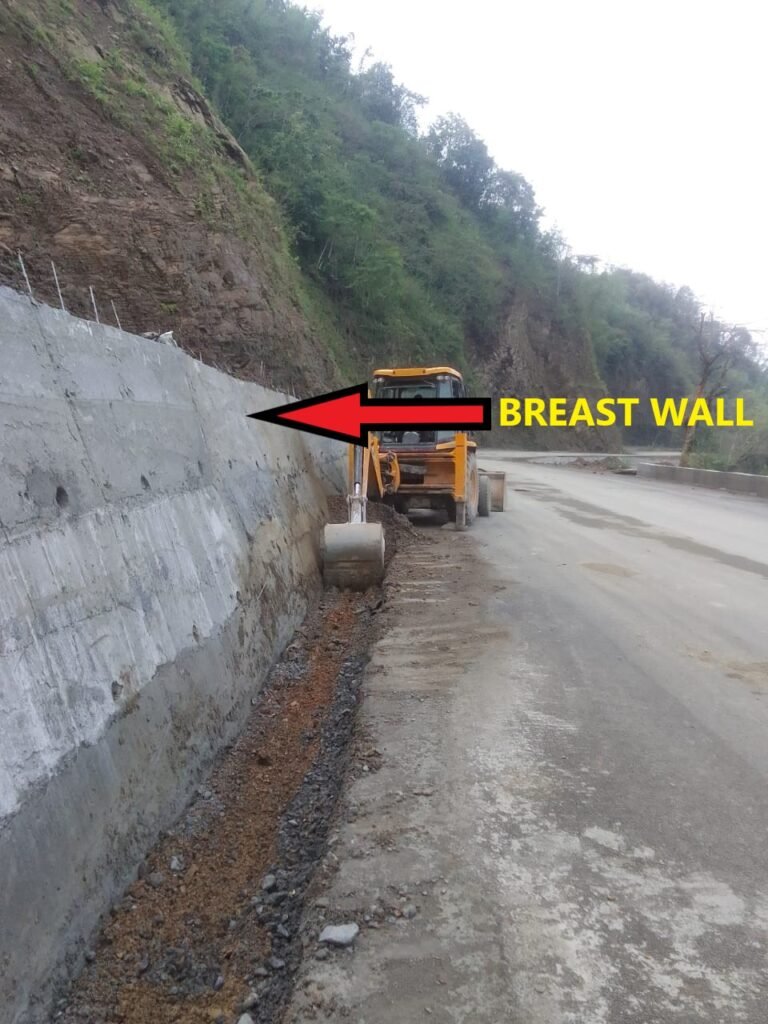

Historical Background of Breast Wall Construction
The origins of breast wall construction trace back through the annals of history, reflecting humanity’s enduring quest to conquer and adapt to challenging landscapes. Ancient civilizations, confronted with the arduous task of traversing hilly terrains, pioneered rudimentary forms of breast walls to secure pathways and trade routes. Constructed with elemental materials such as stones and timber, these early structures laid the groundwork for the sophisticated engineering solutions employed in contemporary breast wall construction.
Over the epochs, breast walls evolved concomitant with advancements in construction techniques and materials. From the awe-inspiring terraced fields of ancient agricultural civilizations, ingeniously constructed to optimize arable land on hillsides, to the intricately designed defensive walls of medieval fortresses that safeguarded strategic vantage points, the historical legacy of breast wall construction attests to human ingenuity in adapting to and harnessing the power of the landscape.
Function of Breast Walls in Hill Road Construction
In the harsh and undulating environments of hill road building, the term “breast wall” carries significant weight. This powerful structure, strategically placed along the hillsides, is critical to ensure the stability, safety, and lifespan of roadways that traverse difficult terrain. Understanding the function of a breast wall reveals its numerous contributions to the intricate tapestry of infrastructure development in mountainous areas.
1. Stabilizing Slopes:
Breast walls stabilize dangerous slopes in hilly terrains. Hillsides are naturally prone to erosion, landslides, and slope failure caused by gravitational forces acting on loose or unconsolidated soil. Breast walls act as a robust countermeasure, providing structural support to prevent the collapse of the hillside onto the road. By distributing the forces and resisting lateral movement, these walls enhance slope stability, ensuring the road’s integrity and safety.
2. Erosion Control:
Hill roads are prone to erosion, particularly during heavy rainfall. This lessens the probability of landslides brought on by saturated soil in along with shielding the roadbed from degradation. The durability and usefulness of hill roadways depend on effective erosion management, which makes breast walls a crucial component of sustainable infrastructure.
3. Safety Enhancement:
In hill roadway construction, where rockfalls and landslides are a constantly threat, safety comes firstly. Breast walls work as defensive barriers, reducing the risk of loose pebbles or debris falling on the road. These structures promote road safety by confining possible hazards, reducing the risks connected with natural forces that can endanger the well-being of road users.
4. Creating Stable Foundations:
A well-designed breast wall contributes to the creation of a stable foundation for the road. A well-constructed breast walls helps establish a solid foundation for the road. The support given through the wall enables the construction of roads on hillsides that would otherwise be unfeasible or dangerous. The flat surface created by the breast wall makes it easier to lay roadbed materials, resulting in a stable foundation that can endure the hillside’s dynamic stresses.
5. Adaptation to Varied Terrain:
Hill road construction often encounters diverse and challenging topographies. Breast walls are versatile structures that can be adapted to different terrains, including steep slopes, uneven surfaces, and areas with varying geological conditions. This adaptability makes them indispensable in the engineer’s toolkit when crafting roads through landscapes that would otherwise be arduous to navigate.
SUMMARY
In the intricate dance between engineering precision and environmental dynamics, breast walls emerge as stalwart guardians of hill road construction. Their function extends beyond mere physical barriers; they represent a dedication to safety, sustainability, and adaptation in the face of natural forces. As hill road infrastructure expands, breast walls play an increasingly important role in ensuring that these difficult terrains are not only navigable, but also safe and long-lasting for future generations.
Common Materials Used in Breast Wall Construction
Breast walls’ adaptability is reflected in the wide range of materials used in their construction, each carefully chosen based on factors such as geological conditions, structural needs, and aesthetic concerns.
Reinforced Concrete:
A stalwart in modern construction, reinforced concrete emerges as a preeminent material for breast walls. The strong combination of concrete’s compressive strength and steel’s reinforcing qualities creates a durable system that can withstand the pressures of hillsides. This material not only stays structurally resilient but also adapts to changes in the terrain.
Natural Stone:
Using natural stone for breast wall construction is a classic choice that connects to the past. The stones, sourced locally, add strength to the wall and harmonize with the surroundings, creating a seamless link between the man-made structure and the natural scenery.
Gabions:
Gabions, which are wire mesh baskets filled with stones, are a practical solution in situations where flexibility and permeability are important. The flexibility of gabion breast walls helps with drainage control, which in turn reduces hydrostatic pressure and lowers the risk of erosion. This approach showcases a delicate balance between structural efficacy and environmental compatibility.
SUMMARY
As we delve deeper into the complexities of breast wall construction, a fascinating tapestry emerges, woven with strands of engineering expertise, historical sagacity, and an unwavering commitment to harmonizing human infrastructure with the undulating landscapes it seeks to conquer. The following sections will delve into the design principles, building techniques, and environmental issues that distinguish contemporary breast wall construction procedures, providing a thorough understanding of this crucial aspect of civil engineering.
Factors Influencing Breast Wall Design
Breast walls are remarkable engineering feats in the challenging realm of hill road construction, providing stability and support to land filled with steep slopes and natural instability. Their effectiveness lies not only in their physical form, but also in the intricate design principles that guide their creation. This piece examines the various factors that impact breast wall design, uncovering the intricacies that engineers face in constructing strong and long-lasting structures.
Geological Conditions:
The geological makeup of a site is a cornerstone in breast wall design. Engineers conduct comprehensive site surveys in order to assess the characteristics of the soil, rock formations, and potential geohazards. The design requirements are significantly influenced by the angle of repose, cohesion, and internal friction of the soil, which are crucial factors to consider. To ensure the stability of the retaining wall against the natural forces exerted by the hillside, engineers must develop tailored design strategies that account for the diverse geological conditions.
Topography and Slope Geometry:
The topography of the terrain and the slope geometry play pivotal roles in determining the design of breast walls. Steeper slopes necessitate more robust and vertically oriented walls to counteract gravitational forces. The alignment and curvature of the road also influence the design, requiring adjustments to ensure optimal support and stability. In situations where the slope is irregular or uneven, engineers must adapt the design to accommodate these variations.
Height and Load-Bearing Requirements:
The height of the breast wall and the anticipated load it will bear are fundamental considerations in design. Additional reinforcement is necessary for taller walls or walls that support heavy loads. This reinforcement often comes in the form of buttresses or tiebacks. The selection of materials and construction methods is directly influenced by the structural demands imposed by the height and load-bearing requirements. A thorough structural analysis is conducted to ensure that the wall can safely bear the applied loads.
Hydrological Considerations:
Water is a formidable force that can compromise the stability of breast walls. To prevent the accumulation of water behind the wall, which may lead to hydrostatic pressure and failure, it is essential to integrate efficient drainage systems into the design. In order to effectively manage the flow of water and minimize the risk of erosion, the design should encompass features such as weep holes, drainage pipes, or graded backfill.
Environmental Impact and Aesthetics:
Breast walls not only add beauty to the landscape but also serve a practical function. Engineers need to find a harmonious balance between usefulness and environmental impact, considering the ecological footprint of construction materials and methods. Additionally, the design should seamlessly blend with the natural surroundings, ensuring that the breast wall becomes one with the scenery.
Material Selection:
The choice of materials significantly influences breast wall design. Reinforced concrete, natural stone, and gabions are frequently utilized materials in the construction industry. Each material presents unique benefits and obstacles, and the choice is influenced by various factors including cost, local accessibility, and the specific needs of the site. Engineers must meticulously evaluate the characteristics of these materials to guarantee they fulfill the structural and environmental criteria of the breast wall.
Seismic Considerations:
Engineers working in regions prone to earthquakes need to consider the impact of dynamic forces caused by seismic activity. It is crucial to incorporate seismic design principles, including the utilization of flexible materials and meticulous planning of foundation construction, to guarantee that the retaining wall can withstand seismic forces and prevent disastrous collapse.
SUMMARY
Breast wall design involves a comprehensive analysis of geological, topographical, hydrological, and environmental factors. By considering the interplay of these elements, along with meticulous material selection and adherence to structural principles, breast walls can be created that not only fulfill their primary purpose but also stand as enduring symbols of engineering excellence in challenging landscapes. As technology and understanding evolve, the continued refinement of breast wall design ensures the creation of resilient and sustainable infrastructure in hill road construction.
Geological Factors and Breast Wall Design in Hill Road Construction
The construction of breast walls in hill road projects represents a delicate equilibrium between human engineering prowess and the dynamic forces of nature. Geological factors play a pivotal role in shaping the design decisions of breast walls, influencing choices related to material selection, structural integrity, and overall stability. Understanding how geological considerations impact breast wall design is essential for creating robust structures capable of withstanding the challenges posed by the diverse terrains of hilly landscapes.
1. Soil Composition:
The geological composition of the soil plays a critical role in influencing the stability of the hillside and the design of breast walls. Engineers conduct thorough soil analyses to evaluate key factors such as cohesion, internal friction, and angle of repose. The design approaches for sandy or loose soils may vary from those required for cohesive or rocky soils. The choice of materials, reinforcement techniques, and the angle of the wall are all influenced by the specific characteristics of the soil, ensuring that the breast wall can effectively counteract gravitational forces.
2. Rock Formations:
In regions with substantial rock formations, the geological structure impacts both the excavation process and the design of breast walls. Engineers need to evaluate the rock type and stability on the hillside in order to decide whether blasting or rock-cutting is needed. The breast wall design might have to be adjusted to deal with any irregularities in the rock face, and factors like rock anchoring may need to be taken into account to establish a strong link between the wall and the underlying rock layers.
3. Seismic Activity:
Hilly terrains are often situated in seismically active zones, adding an additional layer of complexity to breast wall design. The geological risk of earthquakes influences decisions regarding the wall’s flexibility, foundation design, and overall structural resilience. Engineers implement seismic design principles to ensure that retaining walls can withstand the dynamic forces generated by an earthquake, preventing catastrophic failure and ensuring the safety of the infrastructure.
4. Groundwater Conditions:
Geological factors also significantly influence groundwater conditions, which can have a profound impact on the stability of breast walls. Water can have a detrimental effect on soil strength and cause an increase in hydrostatic pressure behind the wall. To mitigate this, engineers need to take into account the groundwater levels and incorporate efficient drainage systems like weep holes or drainage pipes. These measures are crucial in preventing water buildup and reducing the chances of erosion or structural failure.
5. Geological Hazards:
Dealing with geological hazards like landslides and rockfalls can be quite challenging when designing breast walls. By studying the history of geological events in the region, engineers can better prepare for potential risks. Implementing reinforcement techniques, such as soil nails or rock bolts, can help improve the wall’s ability to withstand these natural challenges.
SUMMARY
Geological factors wield a profound influence on the design decisions surrounding breast walls in hill road construction. The intricate dance between human engineering acumen and the inherent characteristics of the terrain shapes the blueprint of these structures. A comprehensive comprehension of soil composition, rock formations, seismic risks, groundwater conditions, and geological hazards is essential for constructing breast walls that not only endure the natural forces in action but also guarantee the safety and durability of hill road infrastructure. As geological science and engineering progress, the development of breast walls will unquestionably transform, demonstrating an ongoing dedication to overcoming nature’s obstacles through innovation and resilience.
What is the difference between Breast wall and Retaining wall?
Breast walls and retaining walls serve the common purpose of managing slopes and ensuring stability in hilly or uneven terrains. Despite their similarities, these structures exhibit unique differences in terms of their intended functions, structural designs, and practical applications.
- Purpose:
Breast Wall:
Purpose: Breast walls are mainly constructed to withstand horizontal pressures and offer stability to the embankment or road on one side. They are frequently utilized in hill road building to reinforce slopes and prevent soil erosion.
Retaining Wall:
Purpose: Retaining walls are built to hold back soil on both sides, serving the purpose of creating level surfaces on sloped terrain, preventing erosion, and enabling the construction of structures such as terraced gardens, parking lots, or building foundations.
- Structural Design:
Breast Wall:
Design: Breast walls are typically smaller in height and are designed to bear loads from one side only. They may have a batter (slope) facing the hillside for added stability but are not required to support loads from both sides.
Retaining Wall:
Design: Retaining walls are larger structures designed to withstand the lateral pressure of soil on both sides. They often have a thicker cross-section and are engineered to resist the forces acting from behind the wall.
- Load-Bearing Considerations:
Breast Wall:
Load-Bearing: Breast walls primarily bear the weight of the hillside or embankment, preventing it from collapsing onto the road or structure below.
Retaining Wall:
Load-Bearing: Retaining walls bear the weight of the soil or other backfill material on both sides. They must resist the lateral earth pressure generated by the retained soil.
- Application:
Breast Wall:
Application: Commonly used in hill road construction, breast walls are strategically placed along the slope to stabilize it and protect the road from landslides and erosion.
Retaining Wall:
Application: Retaining walls find applications in various settings, including landscaping, residential construction, and commercial developments. They are used to create terraced gardens, level building pads on hillsides, or support structures built on sloped terrain.
- Aesthetic Considerations:
Breast Wall:
Aesthetics: While aesthetics are considered, the primary focus of breast walls is functionality and stability in hill road construction. They may blend with the natural surroundings but are often more utilitarian in appearance.
Retaining Wall:
Aesthetics: Retaining walls are often designed with aesthetics in mind, especially when used in residential landscaping. They come in various materials and finishes to complement the overall design of the landscape.
SUMMARY
In summary, breast walls and retaining walls serve distinct purposes in managing slopes and uneven terrain. Breast walls are specialized structures designed to stabilize slopes and protect roads in hilly areas, while retaining walls have a broader range of applications and are designed to hold back soil on both sides to create level surfaces. The key differences lie in their load-bearing functions, structural designs, and intended applications.
Conclusion
Exploring the complexities of breast wall construction reveals a multifaceted tapestry blending engineering knowledge, historical wisdom, and a dedication to integrating human structures with the natural environment. Following sections will discuss design principles, construction methods, and environmental factors shaping modern practices in breast wall construction, offering a thorough examination of this essential aspect of civil engineering.