Hook length is the extra length of steel bar provided at the ends of stirrups and reinforcement bars to form a bend (hook). For a stirrup to work effectively, its ends must be bent into hooks of specific angles—typically 45°, 90°, or 135°, as recommended by IS 2502 and IS 456:2000.
Table of Contents
Why Hook Length Is Important in Stirrups
- Stirrups resist shear forces and Hooks ensure the stirrup bar is anchored properly inside the concrete so it does not slip out under load.
- Stirrups keep main longitudinal bars in position.
- To Resist Seismic (Earthquake) Forces.
- Correct hook length ensures these corners remain locked, preventing corner cracks.
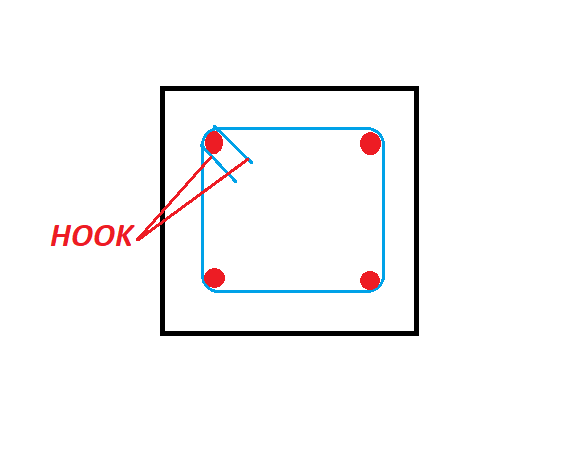
Hook Length for Stirrups (90° & 135° Hooks)
For 90° Hook Stirrups
Hook Length (L)
Hook Length = 10d
Where:
d = diameter of the stirrup bar
For 135° Hook Stirrups
Hook Length (L)
Hook Length = 12d
Where:
d = diameter of the stirrup bar
Deduction for Stirrups (45°, 90°, 135° & 180° Hooks)
For 45° Hook Stirrups, Deduction Length = 1d
For 90° Hook Stirrups, Deduction Length = 2d
For 135° Hook Stirrups, Deduction Length = 3d
For 180° Hook Stirrups, Deduction Length = 4d
Example Calculation
Given:
Beam size = 300 × 450 mm
Cover = 25 mm
Bar diameter = 8 mm (stirrups)
Hook = 135°
Effective stirrup size:
L=300−2(25)=250mm, B=450−2(25)=400 mm
Perimeter:
2(250+400)=1300 mm
Hook Length (135°):
Hook Length =2nos. of hook x 12d =2x12x8 =192 mm
Deduction for Hook (135°):
Deduction Length = 2nos. of hook x 2d = 2*2*8 = 32 mm
Total Stirrup Length:
1300+192-32=1460 mm=1.46 m
Conclusion
Hook length formula ensures proper anchorage of stirrups, improving shear resistance, preventing bar slip, and maintaining structural safety as per IS codes.

