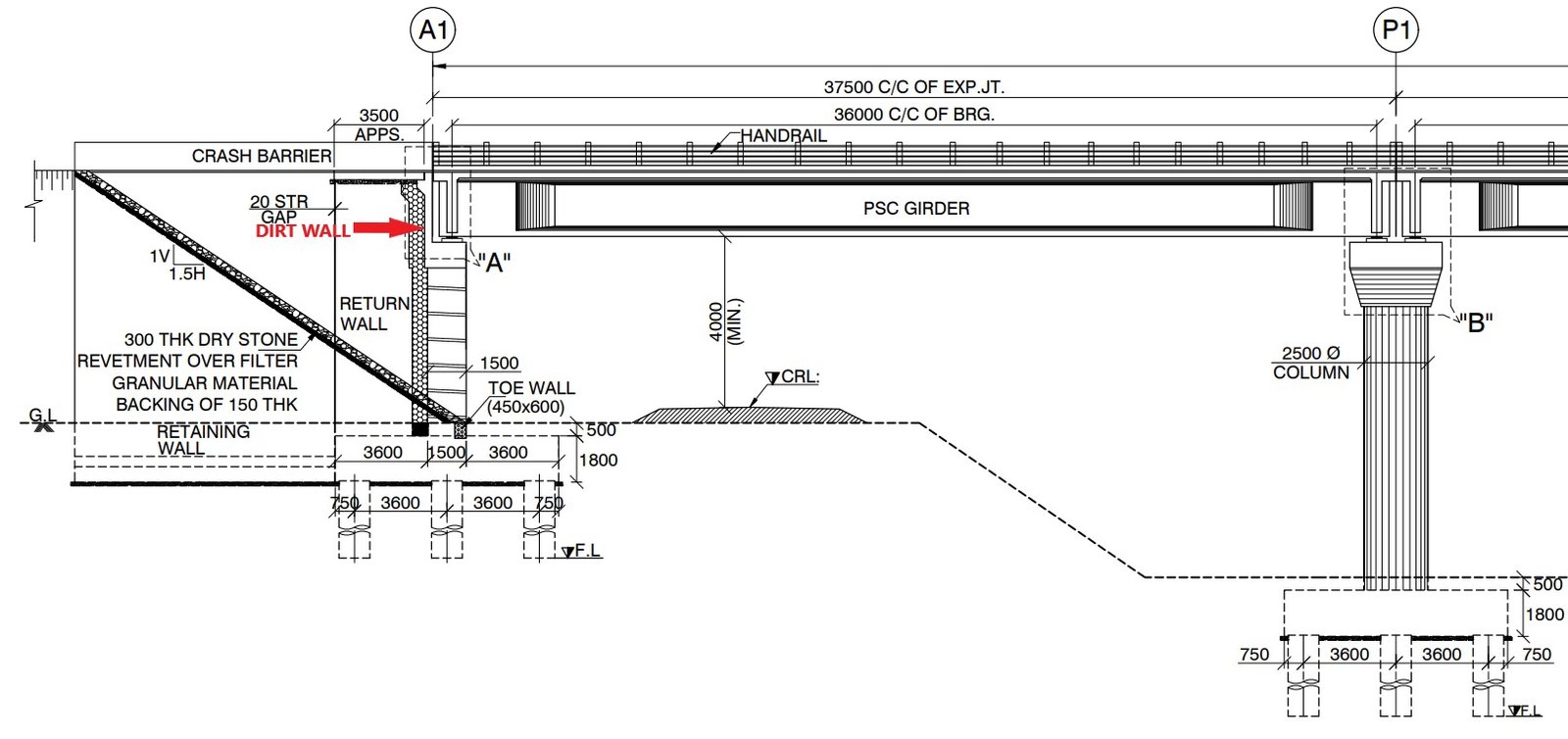
When constructing a bridge, stability and durability are top priorities. One crucial but often overlooked component of bridge abutments is the dirt wall. These walls provide essential support, help prevent soil erosion and contribute to the structure’s long-term strength. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of Dirt Wall in Bridge Abutment, their design and the benefits they bring to bridge construction.
Table of Contents
What is a Dirt Wall in a Bridge?
A Dirt Wall in Bridge Abutment is a type of earth retaining wall used in bridge abutments to provide structural support and prevent soil erosion. It helps distribute loads, stabilize embankments, and blend with the natural environment. These walls can be reinforced with materials such as compacted soil, geotextiles, and concrete to improve strength and durability.
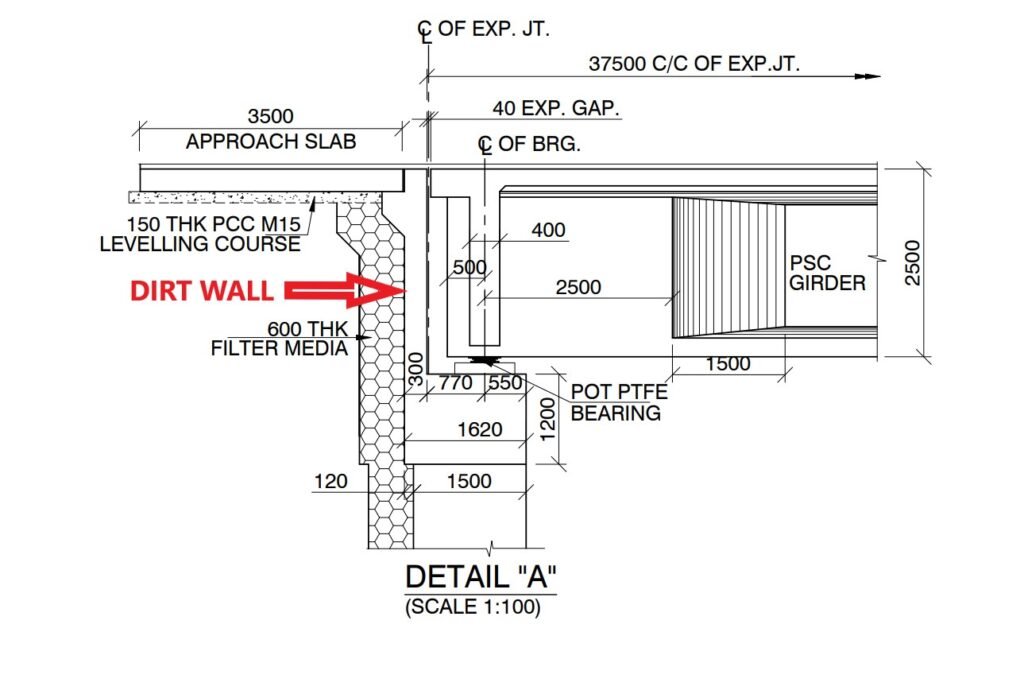
Purpose of Dirt Wall in Bridge Abutment
Dirt wall or earth retaining wall, serve multiple purposes in bridge abutment:
- Stabilizing the Embankments: They prevent soil from shifting due to traffic vibrations or water movement.
- Distributing Load Efficiently: Dirt walls help spread out the bridge’s weight to prevent excessive pressure on any single point.
- Preventing Erosion: They reduce soil loss caused by water runoff, wind, and vehicle activity, preserving the integrity of the bridge.
- Blending with the Environment: Sometimes, these walls are designed to accommodate vegetation, making the bridge look more natural while reducing its environmental impact.
Design Considerations for Dirt Wall in Bridge Abutment
The design of a dirt wall varies depending on several factors, including soil type, load capacity, and environmental conditions. Some of the critical elements engineers consider include:
- Choosing the Right Materials: The walls are typically built using compacted soil, geotextiles, reinforced concrete, or a mix of these materials for added strength.
- Ensuring Proper Drainage: To prevent water buildup, drainage solutions like weep holes and geotextile fabrics are added to manage hydrostatic pressure.
- Compact and Layered Construction: Engineers compact the soil in layers to enhance stability and reduce settlement over time.
- Additional Support Structures: Dirt walls may be reinforced with Gabion walls, Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE) walls, or stone masonry to improve durability.
Construction Process of Dirt Wall in Bridge Abutment
The construction of dirt walls involves several essential steps to ensure structural integrity and long-term stability. Below is a step-by-step process for building a dirt wall from pile foundation to final construction:
1. Pile Foundation Construction:
- Drill boreholes and install reinforced concrete piles to provide deep foundation support.
- Ensure piles reach stable soil or rock strata to bear the bridge loads efficiently.
- Pour concrete and allow it to cure before moving to the next step.
2. Pile Cap Construction:
- Construct a reinforced concrete pile cap to distribute loads evenly across the piles.
- Use formwork and reinforcement bars to provide structural stability.
- Pour concrete and ensure proper curing before proceeding.
3. Abutment Construction:
- Erect abutments using reinforced concrete, stone masonry, or Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE) walls.
- Ensure proper alignment and reinforcement to support bridge loads.
- Install expansion joints as needed to accommodate structural movement.
4. Abutment Cap Construction:
- Construct the abutment cap on top of the abutment to transfer loads from the bridge deck to the abutment walls.
- Reinforce with steel bars and high-strength concrete for additional support.
- Allow sufficient curing time before placing the superstructure.
5. Dirt Wall Construction:
- Excavate and prepare the base for the dirt wall.
- Place granular sub-base material and compact it to improve stability.
- Construct the dirt wall in layers, compacting soil at each stage to prevent settlement.
- Use geotextiles, geogrids, or MSE reinforcements between layers to enhance stability.
- Ensure proper drainage by installing weep holes, geotextile filters, and drainage pipes to manage hydrostatic pressure.
6. Finishing and Protection:
- Apply stone pitching, vegetation, or concrete facing to prevent erosion and enhance durability.
- Perform final grading and compaction to ensure a smooth transition between the dirt wall and the surrounding embankment.
- Conduct quality control checks to confirm structural integrity and stability.
Benefits of Dirt Wall in Bridge Abutment
- Cost-Effective Solution: Compared to concrete retaining walls, dirt walls are more economical, especially in areas with readily available soil.
- Ease of Construction: With proper engineering techniques, dirt walls can be constructed quickly, minimizing project delays.
- Eco-Friendly: They allow for better water absorption and can support vegetation growth, reducing environmental impact.
- Enhanced Safety: By preventing soil displacement, dirt walls contribute to the overall stability of the bridge abutment, ensuring safety for commuters.
Conclusion
Dirt walls play a vital role in bridge abutment construction, though they often go unnoticed. They help stabilize the structure, prevent erosion, and improve the bridge’s longevity. Thanks to advancements in engineering, modern dirt walls now include innovative reinforcements to enhance safety and meet environmental standards. A well-designed dirt wall ensures the bridge remains secure and durable, making it an essential element of sustainable infrastructure.