In India, the Indian Roads Congress (IRC) sets guidelines for the design and construction of roads. A major part of this is the four lane road, which is essential for the country’s transport network, facilitating the efficient movement of goods and people across cities, towns and states. This article examines the width specifications and various factors that influence the design of 4 lane road width in India.
Table of Contents
What is the Width of a 4 Lane Road in India?
The standard width of a 4 lane road in India, according to the Indian Roads Congress (IRC) guidelines, is generally 14 meters for the carriageway, with each lane measuring 3.5 meters. When accounting for a median that varies from 1.2 to 5 meters and paved shoulders that range from 1.5 to 2.5 meters on either side, the overall width of the road can vary between 20 and 25 meters, contingent upon the specific design and geographical context of the roadway.
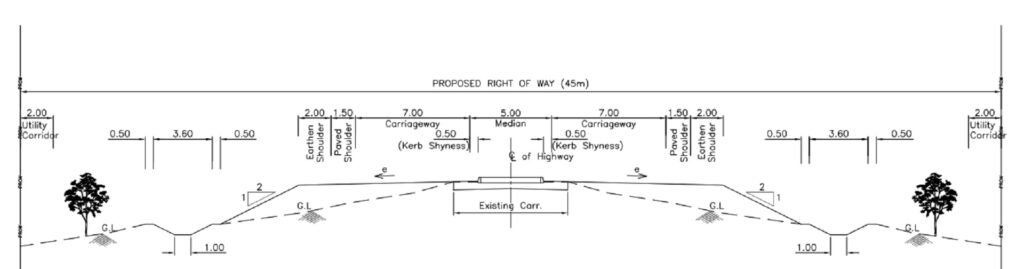
Width of a 4 Lane Road in India
A 4 lane road comprises two lanes in each direction, separated by a median for safety. According to the IRC guidelines, the 4 lane road width standard in India are:
- Lane Width:
Each lane should be 3.5 meters wide. For a 4 lane road, this totals to:
7 meters (two lanes) on each carriageway. - Median Width:
The median separating the two carriageways can range from 1.2 to 5 meters, depending on the road’s classification and surrounding conditions. Wider medians are preferred for high-speed roads as they enhance safety and can accommodate future expansions. - Shoulder Width:
Shoulders are provided on both sides of the road for vehicle stoppage and safety. These are categorized as: - Paved Shoulders:
Typically 1.5–2.5 meters wide.
Earthen Shoulders: 1–2 meters wide, usually unpaved. - Total Width:
For an undivided 4-lane road, the total width is approximately 15–16 meters, including shoulders.
For a divided 4-lane road, the total width is around 20–25 meters, including shoulders and the median.
Standard Width of National Highways in India
Below is a detailed table showing the specifications for 2 lane, 3 lane, 4 lane, 6 lane, and 8 lane road construction in India as per IRC guidelines. It includes dimensions for carriageway width, median and shoulders.
| Road Type | Carriageway Width | Median Width | Paved Shoulder Width | Earthen Shoulder Width | Total Width (Approx.) | Right of Way (ROW) | Future Expansion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Lane Road | 7.0 m (3.5 m/lane) | Not applicable | 1.5–2.5 m (both sides) | 1.0–2.0 m (both sides) | 12.0–14.0 m | 30–45 m | Can be expanded to 4 lanes |
| 3-Lane Road | 10.5 m (3.5 m/lane) | Not applicable | 1.5–2.5 m (both sides) | 1.0–2.0 m (both sides) | 15.0–17.0 m | 30–45 m | Rarely used; may convert to 4 lanes |
| 4-Lane Road | 14.0 m (3.5 m/lane) | 1.2–5.0 m | 1.5–2.5 m (both sides) | 1.0–2.0 m (both sides) | 20.0–25.0 m | 45–60 m | Can be expanded to 6 lanes |
| 6-Lane Road | 21.0 m (3.5 m/lane) | 2.0–6.0 m | 2.0–3.0 m (both sides) | 1.5–2.0 m (both sides) | 30.0–36.0 m | 60–75 m | Can be expanded to 8 lanes |
| 8-Lane Road | 28.0 m (3.5 m/lane) | 2.0–6.0 m | 2.0–3.0 m (both sides) | 1.5–2.0 m (both sides) | 38.0–45.0 m | 75–90 m | Sufficient capacity; may add service roads |
Factors Influencing 4 Lane Road Width
The exact width of a 4 lane road in India may vary based on several factors:
- Type of Road: Roads under the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) are built to higher standards than local roads, with a focus on safety, speed, and durability.
- Traffic Volume: Higher traffic volumes may require wider lanes, medians, and shoulders.
- Urban vs. Rural Areas: Urban roads often face space constraints, leading to narrower shoulders and medians compared to rural roads.
- Topography: Roads in hilly areas may have reduced shoulder widths due to space and terrain limitations.
Importance of Proper 4 Lane Road Width Design
The width of a 4 lane road is crucial for:
- Traffic Safety: Adequate width reduces the risk of accidents by providing ample space for vehicles and pedestrians.
- Traffic Flow: Properly designed widths ensure smooth movement of vehicles, reducing congestion.
- Future Expansion: Wider roads and medians allow for easy expansion to 6-lane or 8-lane highways if required.
Conclusion
The construction of a 4 lane road width in India follows established IRC standards, which ensure uniformity, safety, and operational efficiency. These roads play a pivotal role in improving connectivity and supporting India’s economic growth. With increasing focus on infrastructure development, adherence to these standards is essential for sustainable and robust road networks across the country.

